Lean Production is widely recognized and accepted in the industrial setting. It concerns the strict integration of humans in the manufacturing process, a continuous improvement and focuses on value-adding activities by avoiding waste. However, a new paradigm called Industry 4.0 or the fourth industrial revolution has recently emerged in the manufacturing sector. It allows creating a smart network of machines, products, components, properties, individuals and ICT systems in the entire value chain to have an intelligent factory.
The connection is their common goal – operational excellence
For several decades, manufacturers have used lean principles and tools to reduce operational complexity and improve productivity. The lean approach provides the foundation for operational excellence by standardizing processes, instilling a culture of continuous improvement, and empowering workers on the shop floor. However, given the increasing complexity of operations, many companies have found that lean management by itself is not sufficient to address their operational challenges. Recently, a set of advanced digital technologies known as Industry 4.0 has emerged to offer new approaches for dealing with complexity and improving productivity. By deploying the right combination of technologies, manufacturers can boost speed, efficiency, and coordination and even facilitate self-managing factory operations. Both approaches have the same goal, which is operational excellence.
The difference is their path & tools to the common goal
Both lean management and Industry 4.0 support the objectives of operational excellence, but they apply different types of tools to achieve these goals. Lean management approach reduces complexity and cost by eliminating waste and non-value-adding activities throughout a process or value chain. It provides techniques for involving all employees in continuously reviewing and improving efficiency. The approach is built on such management techniques as waste reduction,
Industry 4.0 (“The fourth wave of technological advancement in manufacturing”) is powered by nine foundational technologies: additive manufacturing, advanced robotics, augmented reality, big data and analytics, cloud computing, cybersecurity, horizontal and vertical system integration, the industrial internet, and simulation. Sensors, machines, workpieces, and IT systems are connected along a value chain that extends beyond a single enterprise. These connected systems can interact and analyze data to predict failure, reconfigure themselves, and adapt to change. Manufacturers can reach new levels of operational performance. They can, for example, advance from preventive to predictive maintenance, which means that maintenance tasks are performed only when necessary.

Industry 4.0 also allows companies to share the benefits of automation technology more broadly within the organization by, for example, equipping and training line workers to receive and apply real-time information about their machinery. By increasing transparency, improving predictability, and, ultimately, allowing for self-controlled systems, Industry 4.0 promotes faster, more flexible, and more efficient processes. Manufacturers can apply these benefits to achieving the broader objectives: producing higher-quality goods and reducing costs.
Stronger together – Lean Industry 4.0
Manufacturers seeking to optimize their operations need to understand the interplay between traditional lean management and Industry 4.0. Several studies of operational excellence programs in recent years have seen companies generate valuable synergies by implementing lean management and Industry 4.0 holistically, rather than independently or sequentially. Indeed, in most cases, the integrated application of lean management and Industry 4.0—which we call Lean Industry 4.0—is the most effective way to reach the next level of operational excellence. Manufacturers that have successfully deployed Lean Industry 4.0 can reduce conversion costs by as much as 40% in five to ten years—considerably better than the reductions captured by the best-in-class independent deployment of lean or Industry 4.0. To capture the greatest benefits, a manufacturer must tailor the application of Lean Industry 4.0 to address its specific challenges along the supply chain and at the plant level.
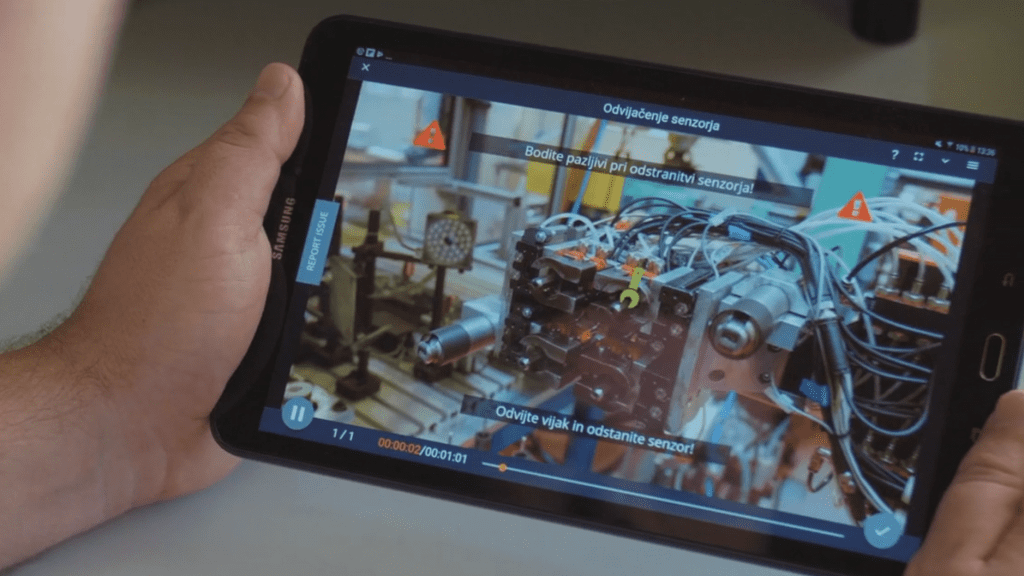
How can REWO help?
REWO is a digital visualization platform, which drastically improves capturing, visualizing and communicating knowledge to anyone within the company’s ecosystem with the use of instructional augmented guides. After you define the process of lean production, REWO will help you communicate the right work operations to your workforce.
